InspiWaveTM
Clinical Evidence

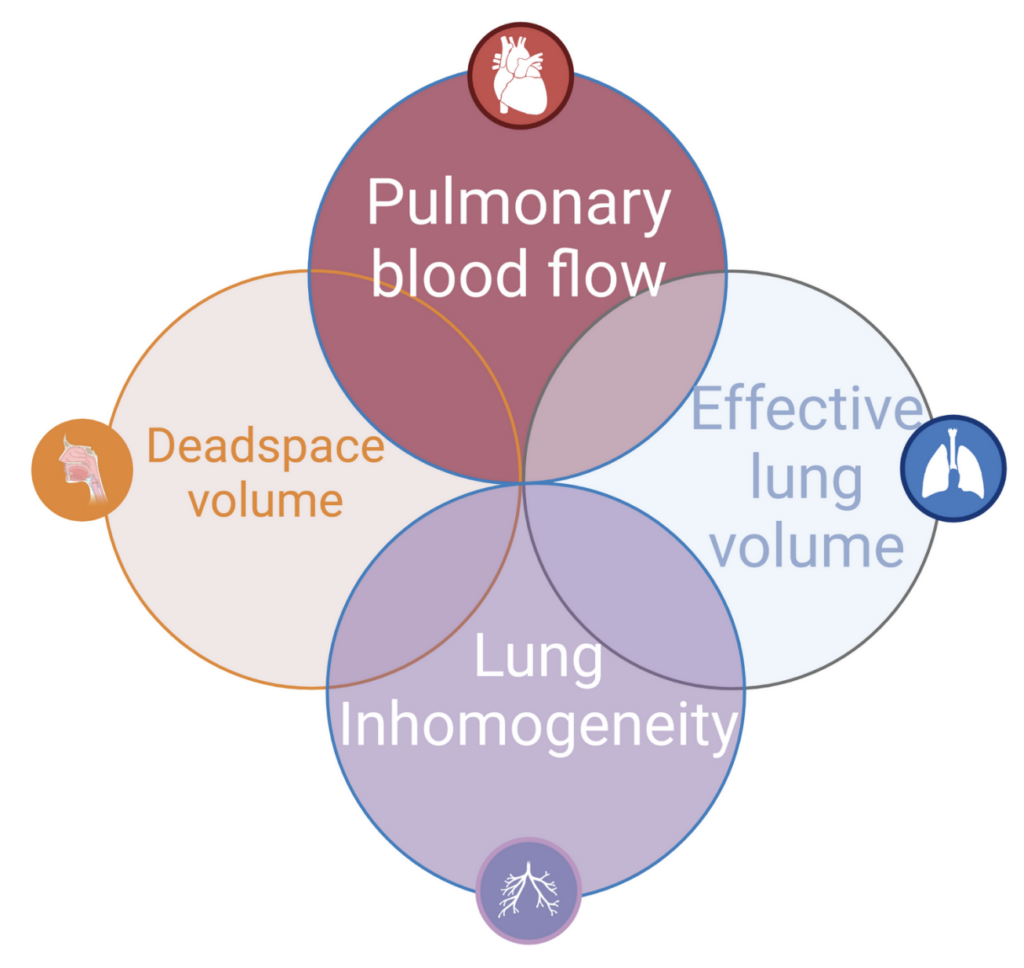
We have completed the R&D phase. In a controlled R&D environment, we have the capability of the device to measure dead space, effective lung volume, pulmonary blood flow, and lung inhomogeneity on a wide range of subjects: artificial lung, volunteers, patients in operating theatres, ICUs, and lung function labs, COPD outpatients, and piglets.
The results of these validation tests have been reported in 10 high-ranking peer reviewed scientific publications. More details of our clinical evidence and the list of our publications can be found here.
- Assessment of lung function in patients with COPD using the Inspired Sinewave Technique
- Validating the inspired sinewave technique to measure the volume of the “baby lung” in a porcine lung injury model
- The Inspired Sinewave Technique A Comparison Study With Body Plethysmography In Healthy Volunteers
- The inspired sine-wave technique – A novel method to measure lung volume and ventilatory heterogeneity
- Simulation-based optimisation to quantify heterogeneity of specific ventilation and perfusion in the lung by the Inspired Sinewave Test
- Measurement of Heart and Lung Function in Neurocritical Care Using the Inspired Sinewave Technique

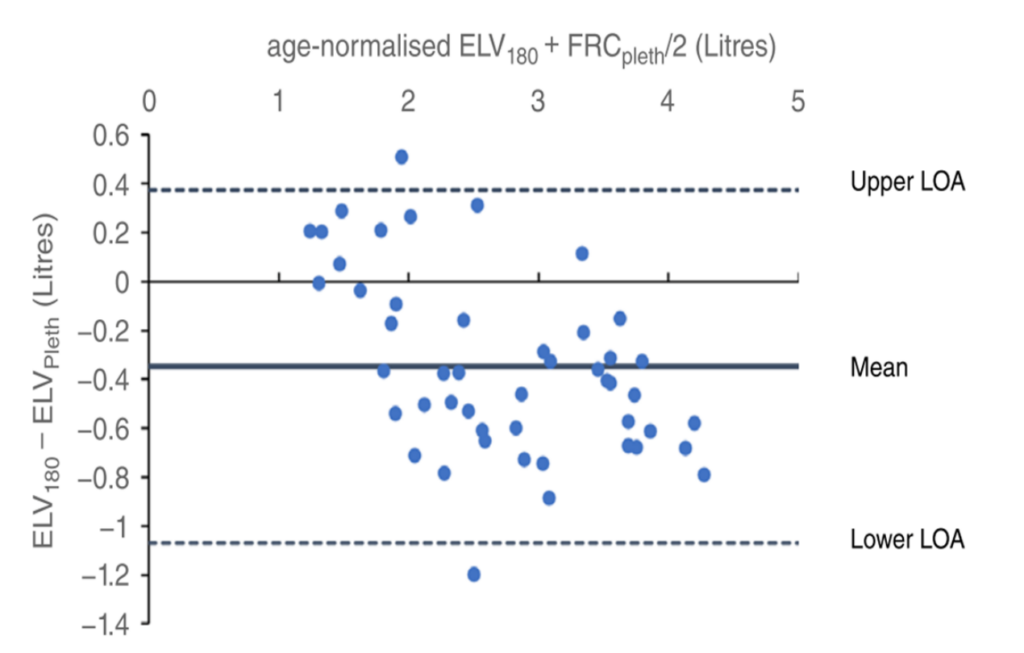
The Bland – Altman plot analysis showed strong agreement between InspiWaveTM and Body Plethysmograph , in measuring effective lung volume
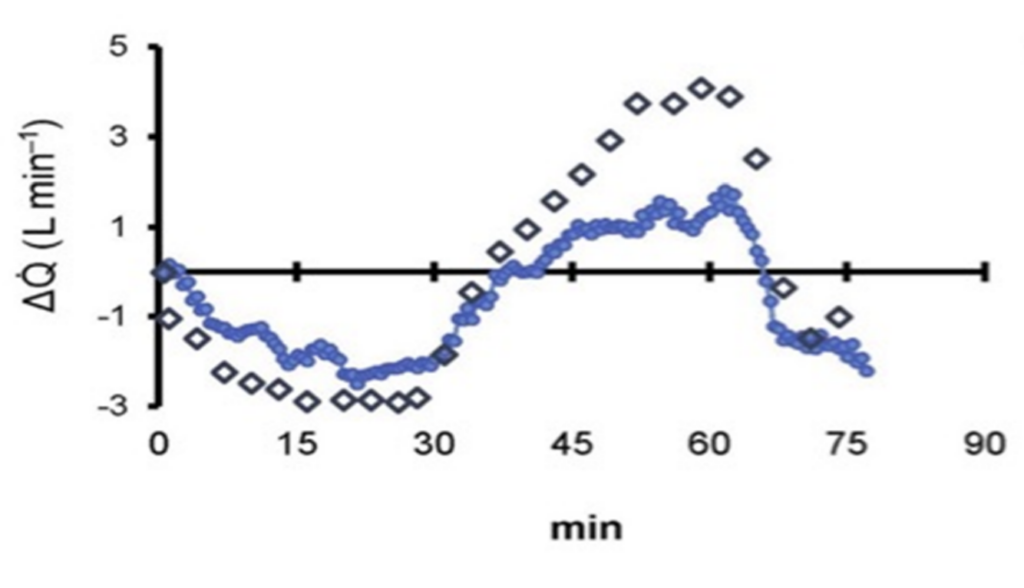
strong agreement (92.5 %) between InspiWaveTM and intermittent measurements by the “gold standard” – thermodilution
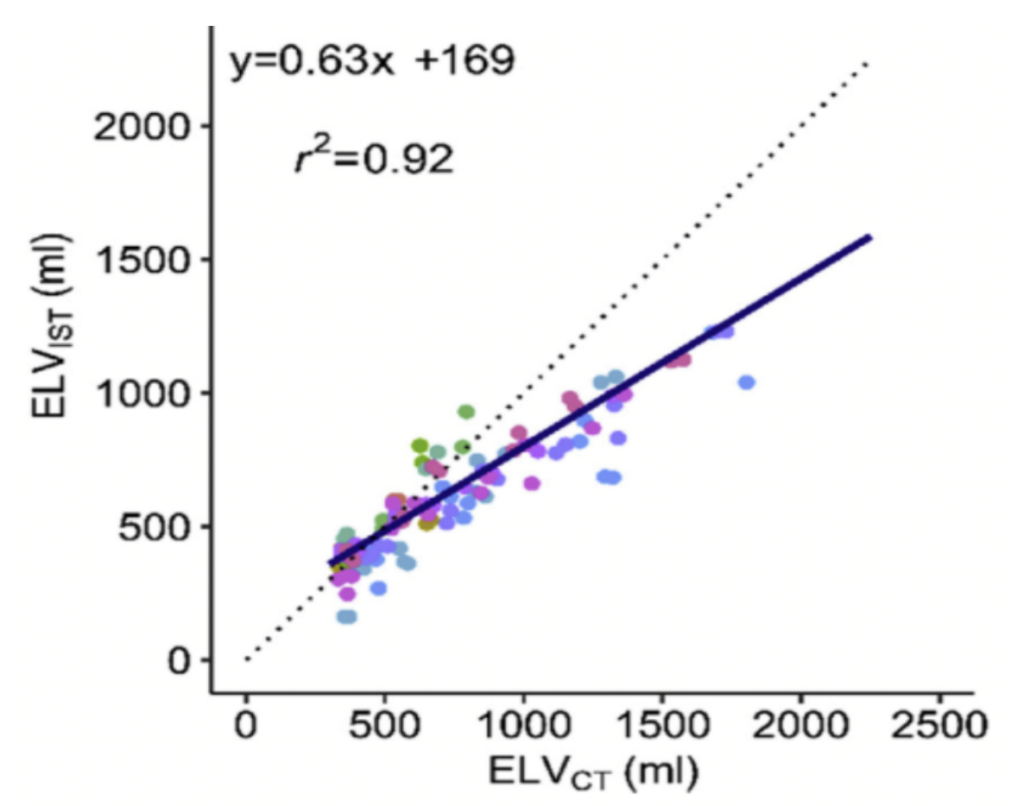
strong correlations between InspiWaveTM (IST) and SF6/CT in measuring lung volume, with R2 of 0.87 and 0.92 respectively.
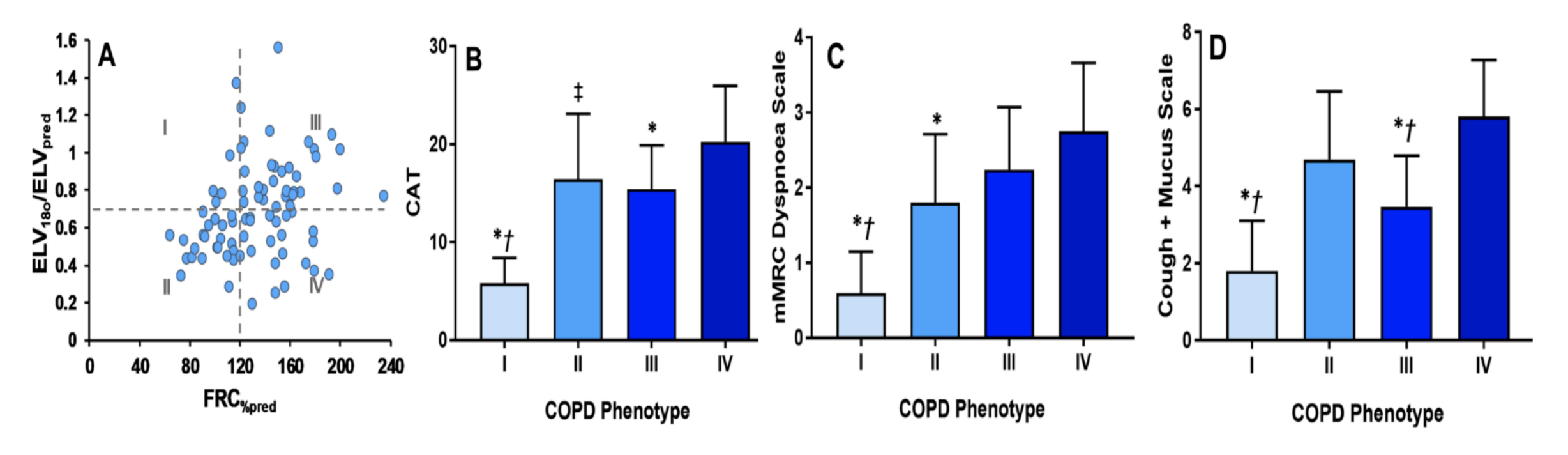
InspiWaveTM‘s index of lung inhomogeneity was a superior predictor of COPD severity vs FEV 1%, and classification vs standard symptom severity questionnaires.